Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 8 is an important year in a student’s life and Maharashtra State Board Science is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 8 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Book syllabus.

Q1. Who am I?
a. I am ATP producing factory.
b. I am single layered, but maintain cellular osmotic pressure.
c. I support the cell, but I am not cell wall. I have a body resembling net.
d. I am chemical factory of the cell.
e. Leaves are green because of me.
Answer a: Mitochondria –Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles present in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells, that produces adinosine triphosphate (ATP), the main energy molecule used by the cell.
Answer b: Vacuole –Vacuoles are membrane-bound cell organelles present in the cytoplasm and filled with a watery fluid containing various substances.
Answer c: Endoplasmic reticulum –Endoplasmic Reticulum is a complex network of tubular membranes exclusively present in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell.
Answer d: Chloroplasts –Chloroplast is an organelle that contains the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll that captures sunlight and converts it into useful energy, thereby, releasing oxygen from water.
Answer e: Chlorophyll –Pigment imparting green colour to plants.
Q2. What would have happened? If …….
a. RBCs had mitochondria.
b. There had been no difference between mitochondria and plastids.
c. Genes had been absent on the chromosomes.
d. Plasma membrane had not been selectively permeable.
e. Plants lacked anthocyanin.
Answer a: Mitochondria are absent in RBCs. Due to this, the oxygen which is carried by them is not used for themselves.
Answer b: Mitochondria and plastids are the cell organelles present in eukaryotes. Mitochondria are found in all the eukaryotic cells, including plants and animals, whereas plastids are found only in plant cells.
Answer c: A gene is a basic unit of hereditary. So, if genes are absent on the chromosomes, then the offspring fails to look like the parent. Absence of genes will prevent the baby from looking like the parent as the gene is the unit which transfers the characteristics from the parent to the child. It is made up of DNA and is present within a nucleus.
Answer d: If Plasma membrane had not been selectively permeable then any substance can enter the cell which can harm the balance between the cell content and outside environment.
Answer e: In food, the main sources of anthocyanins are berries, such as blackberries, grapes , blueberries etc, and some vegetables such as egg-plants and avocado. If plants lacked anthocyanin, they died.
Q3. Who is odd man among us? Give reason.
a. Nucleolus, mitochondria, plastids, endoplasmic reticulum
b. DNA, Ribosomes, Chlorophyll
Answer a: Plastids because they are not found in animal cells, only found in plant cells.
Answer b: Chlorophyll is odd as DNA and ribosome are found in animals but chlorophyll is found in plants.
Q4. Give functions.
a. Plasma membrane
b. Cytoplasm
c. Lysosome
d. Vacuole
e. Nucleus
Answer a: Following are the important plasma membrane function:
Answer b: One of the major functions of cytoplasm is to enable cells to maintain their turgidity, which enables the cells to hold their shape. Other functions of cytoplasm are as follows:
Answer c: The key function of lysosomes is digestion and removal of waste. Cellular debris or foreign particles are pulled into the cell through the process of endocytosis. The process of endocytosis happens when the cell membrane falls in on itself (invagination), creating a vacuole or a pouch around the external contents and then bringing those contents into the cell. On the other hand, discarded wastes and other substances originating from within the cell are digested by the process of autophagocytosis or autophagy. The process of autophagy involves disassembly or degradation of the cellular components through a natural, regulated mechanism.
Answer d: The important functions of vacuole include:
Storage –A vacuole stores salts, minerals, pigments and proteins within the cell. The solution that fills a vacuole is known as the cell sap. The vacuole is also filled with protons from the cytosol that helps in maintaining an acidic environment within the cell. A large number of lipids are also stored within the vacuoles.
Turgor Pressure –The vacuoles are completely filled with water and exert force on the cell wall. This is known as turgor pressure. It provides shape to the cell and helps it to withstand extreme conditions.
Endocytosis and Exocytosis –The substances are taken in by a vacuole through endocytosis and excreted through exocytosis. These substances are stored in the cells, separated from the cytosol. Lysosomes are vesicles that intake food and digest it. This is endocytosis and it varies in different cells.
Answer e: Following are the important nucleus function:
Q5. Who gives me the colour? (Select the correct option).
| Red tomato | Chlorophyll |
| Green leaf | Carotene |
| Carrot | Anthocyanin |
| Violet | Lycopene |
Answer:
| Red tomato | Lycopene |
| Green leaf | Chlorophyll |
| Carrot | Carotene |
| Violet | Anthocyanin |
Q6. How many types of cells are found in living organisms?
Answer: Cells are similar to factories with different labourers and departments that work towards a common objective. Various types of cells perform different functions. Based on cellular structure, there are two types of cells:
Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic Cells
Q7. Which instrument had you used to observe cells?
Answer: A microscope is an optical instrument used to observe objects that are invisible to the naked eye. It is used to view and study cell structure.
Q8. Describe the structure of the cell?
Answer: The cell structure comprises individual components with specific functions essential to carry out life’s processes. These components include- cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and cell organelles. Read on to explore more insights on cell structure and function.
Cell Membrane
Cell Wall
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Q9. Explain the characteristics of the cell?
Answer: Following are the various essential characteristics of cells:
Q10. Define cell.
Answer: A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. Cells are complex, and their components perform various functions in an organism. They are of different shapes and sizes, pretty much like bricks of the buildings. Our body is made up of cells of different shapes and sizes. Cells are the lowest level of organisation in every life form. From organism to organism, the count of cells may vary. Humans have the number of cells compared to that of bacteria.
Cells comprise several cell organelles that perform specialised functions to carry out life processes. Every organelle has a specific structure. The hereditary material of the organisms is also present in the cells.
Q11. What is cytoplasm?
Answer: The fluid that fills up the cells is referred to as the cytoplasm. It encompasses the cytosol with filaments, ions, proteins, and macromolecular structures and also other organelles suspended in the cytosol. The cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells associates with the cell contents except for the nucleus. But in prokaryotic cells, as they do not possess a defined nuclear membrane, the cytoplasm possesses the genetic material of the cell. The cells, in comparison to the eukaryotes, are smaller and have an uncomplicated arrangement of the cytoplasm.
Q12. What is cell organelles?
Answer: An organelle is a specialized subunit having a specific function within the cell. They are ‘organs of the cell.’ Each organelle has its own lipoprotein membrane. Except nucleus and chloroplast, all other organelles can be seen only with an electron microscope.
Q13. What are the functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Answer: The functions of Endoplasmic Reticulum are:
Q14. Explain Golgi Complex.
Answer: It is made up of 5-8 hollow Fusing vesicles and flat sacs placed parallel to each other.
These sacs are called ‘cisternae’ and are filled with different enzymes. The proteins coming from ER are enclosed in vesicles, which come towards golgi complex via cytoplasm. They fuse with the formation face of the golgi membranes and empty their contents in the cisternae.
As they pass through the cisternae, they are chemically modified with the help of enzymes. They are again packed in the vesicles. These vesicles exit from the maturation face. Thus, cisternae work like a packing department that packs and distributes substances.
Q15. What are the functions of Golgi Complex?
Answer: The functions of Golgi Complex are as follows:
Q16. Explain the functions of mitochondria?
Answer: The functions of mitochondria are:
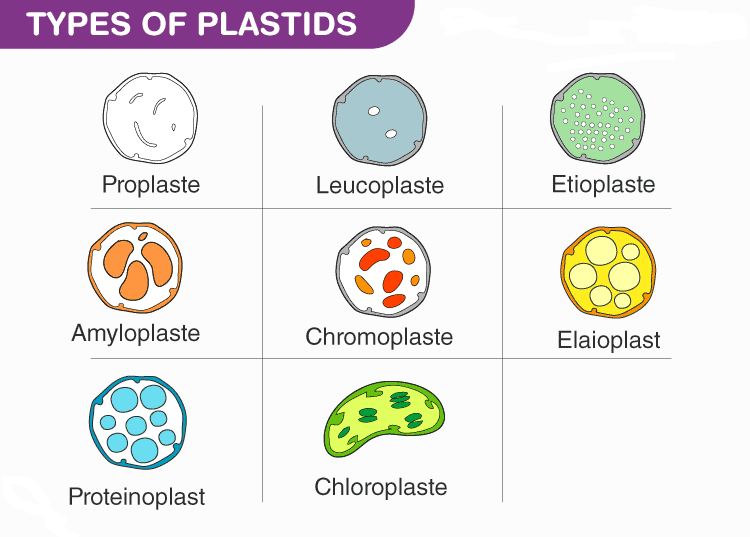
Q17. List the types of Plastids?
Answer: There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among which few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development.
Q18. What is nucleus?
Answer: A nucleus is defined as a double-membraned eukaryotic cell organelle that contains the genetic material. The nucleus is found only in eukaryotes and is the defining characteristic feature of eukaryotic cells. However, some cells, such as RBCs do not possess a nucleus, though they originate from a eukaryotic organism.
Q19. Write the difference between Mitochondria and Plastids.
Answer: The difference between Mitochondria and Plastids
| Mitochondria | Plastids |
| Found in all eukaryotic cells | Found only in plant cells |
| Produces ATP | Produces glucose and stores it as starch |
| The main function is cell respiration | Main organelle for photosynthesis |
| Smaller in size | Comparatively larger in size |
| Pigments are absent | Pigments are present |
Q20. Define vacuole.
Answer: The term “vacuole” means “empty space”. They help in the storage and disposal of various substances. They can store food or other nutrients required by a cell to survive. They also store waste products and prevent the entire cell from contamination. The vacuoles in plant cells are larger than those in the animal cells. The plant vacuoles occupy more than 80% of the volume of the cell. The vacuoles may be one or more in number.
Q21. Define Endocytosis and Exocytosis.
Answer: Endocytosis is defined as the process of trapping a particle or substance from the external environment by engulfing it. Endocytosis is of two types viz phagocytosis, also known as cellular eating and pinocytosis, also referred to as cellular drinking.
Exocytosis, on the other hand, is described as the process of fusing vesicles with the plasma membrane to release their contents to the external environment of the cell.
Q22. Difference between Cell Membrane and Plasma Membrane.
Answer: Following are the important differences between cell membrane and plasma membrane:
| Cell Membrane | Plasma Membrane |
| It surrounds the entire components of the cell. | It surrounds only the cell organelles. |
| It regulates the tonicity of the cell. | It does not regulate the tonicity of the cell. |
| Cell membrane can be transformed to stimulate movement and feeding in organisms such as Paramaecium. | Plasma membrane cannot be modified. |
| It contains initial receptors for signal transduction and is the first step in cell signalling. | It is not the first step in cell signalling. However, it is involved in the process. |
| Always protects the cell from bacteria and viruses. | Does not always protect the cell from outside invaders. |
| Plays an important role in cytokinesis during cell division. | Does not play a key role in cytokinesis during cell division. |
| Cilia are present and are involved in feeding and movement. | Cilia are absent. |
| Is a target for antimicrobials. | Is not a target for antimicrobials. |
Q23. What is osmosis?
Answer: Osmosis is a process by which the molecules of a solvent pass from a solution of low concentration to a solution of high concentration through a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis is of two types: Endosmosis and Exosmosis.
Q24. Define structure of plasma membrane.
Answer: Protein molecules are embedded in two layers of phospholipids. Plasma membrane is said to be a selectively permeable membrane as it allows some substances to enter the cell, while prevents other substances. Due to this property, useful molecules of water, salt and oxygen enter the cell and CO2 exits the cell. If any changes occur outside the cell, the cellular environment does not change due to plasma membrane. This condition is called homeostasis.
Q25. Write the difference between Eukaryotic cells and Prokaryotic cells.
Answer: The differences between Eukaryotic cell Prokaryotic cell are:
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes | |
| Type of Cell | Always unicellular | Unicellular and multi-cellular |
| Cell size | Ranges in size from 0.2 μm – 2.0 μm in diameter | Size ranges from 10 μm – 100 μm in diameter |
| Cell wall | Usually present; chemically complex in nature | When present, chemically simple in nature |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present. Smaller in size and spherical in shape | Present. Comparatively larger in size and linear in shape |
| DNA arrangement | Circular | Linear |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Cytoplasm | Present, but cell organelles absent | Present, cell organelles present |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Plasmids | Present | Very rarely found in eukaryotes |
| Ribosome | Small ribosomes | Large ribosomes |
| Lysosome | Lysosomes and centrosomes are absent | Lysosomes and centrosomes are present |
| Cell division | Through binary fission | Through mitosis |
| Flagella | The flagella are smaller in size | The flagella are larger in size |
| Reproduction | Asexual | Both asexual and sexual |
| Example | Bacteria and Archaea | Plant and Animal cell |